Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes is a disease caused by too little of the hormone insulin or poor use of the body’s insulin. Insulin helps your body use and store glucose (sugar) that comes from food. If insulin levels are low or not working well, sugar builds up in your blood. This causes diabetes and can lead to many problems.
In type 1 diabetes, the body cannot make insulin. In type 2 diabetes, the body does not make enough insulin
or can’t use the insulin well enough to keep the body working well. Most people with diabetes have type 2 dia- betes. Many don’t know they have it.
Type 2 diabetes is usually associated with obesity or overweight.
What are the complications of type 2 diabetes?
People with diabetes are at risk for having serious problems (complications). If your blood sugar level stays too high for too long, complications begin and can include:
-
Blindness
-
Kidney disease and failure
-
Nerve damage and amputation
(loss of toes, fingers or legs)
-
Heart attack and stroke
Many people can control their diabetes with diet, exercise, and medi- cations. Several types of diabetes medications help to improve blood sugar levels for people with type 2 diabetes. Some people with type 2 diabetes may have to take insulin shots so they get enough insulin.
You will need to have your blood tested to learn how well you are controlling your disease. The test used to measure your control over time is the hemoglobin A1c test (A1c).
What is the difference between measuring blood sugar and A1c?
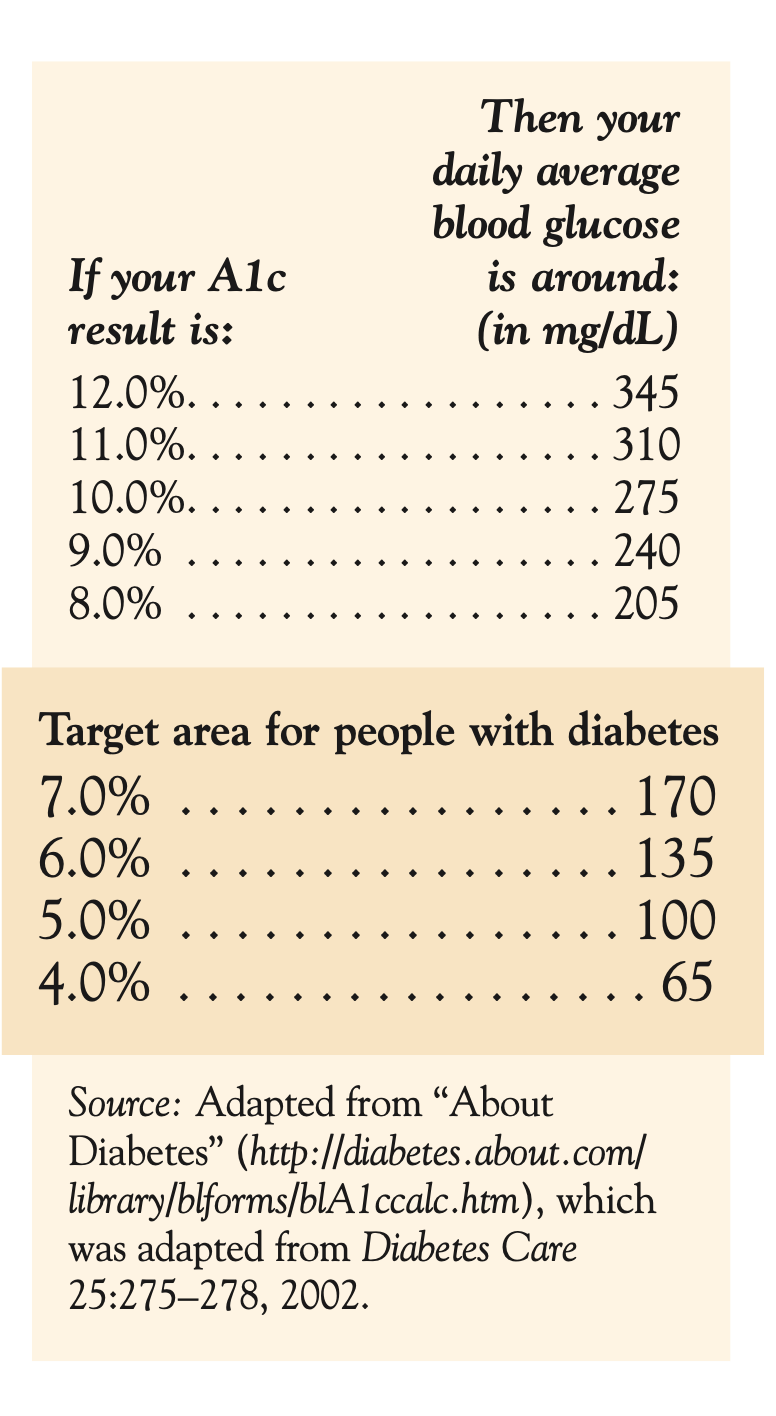
Testing for blood sugar daily tells the level of sugar in your blood at that moment. These levels change all day depending on what and when you eat, whether or not you exercise, and which medications you may be taking. A1c, however, tells information on your sugar control over the past 8 to 12 weeks.
How often should my A1c level be measured?
A1c is measured by a simple blood test performed in a laboratory. Experts recommend that you have your A1c measured four times a year. You can have the test less often if you are controlling your diabetes without medications.
People with diabetes should keep their A1c result below 7% (about 170 mg/dL or less). Studies have shown that people who keep their A1c below 7% greatly reduce their risks of developing long-term complications of diabetes. An average blood sugar for a person without diabetes is 4–6% (about 65–135 mg/dL).
What should I do with this information?
Talk with your doctor if you think you have diabetes. Share your medical and family history so you can get the best treatment. Also, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes eating well, losing weight if needed, exercising, drinking less alcohol and not smoking will help you better manage your diabetes.
Patient Portal
MyHealthRecord Patient Portal allows you to manage appointments, view medications, manage health records, pay your bill, and more.
Patient Resources
We have curated an extensive list of resources for a variety of conditions including adrenal diseases, osteoporosis, thyroid diseases, and much more.
Patient Forms & Info
Patient forms and information about insurance, Medicare, referrals and authorizations, copayments, balances, and more.